Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sn heat treatment
Sn heat treatmentNakajima, Hideo; Hamada, Kazuya; Takano, Katsutoshi*; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Fujitsuna, Nobuyuki*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1145 - 1148, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:77.62(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In ITER, the conductor for the Central Solenoid (CS) uses Incoloy 908, which requires special environment control to prevent cracks caused by Stress Accelerated Grain Boundary Oxidation (SAGBO) during Nb3Sn heat treatment. Use of a stainless steel jacket can simplify the design and fabrication because the special caution is not required for SAGBO. JAERI has already developed high manganese, JK2, whose thermal contraction from 300K to 4 K is almost the same as that of Incoloy: thus no change in the mechanical design of the CS is necessary. However, during the heat treatment, phosphorus enhances embrittlement of JK2. Carbon reduction and boron addition was considered to be a possible solution to mitigate the phosphorus effect. Jackets of low carbon and boron added JK2(JK2LB) were produced and tensile properties, fracture toughness, and crack propagation rate were measured at 4K. Elongation and fracture toughness at 4K after the heat treatment are 33% and 91 MPam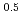 for the final jacket, which satisfy the ITER targets. JK2LB can be applied to the ITER CS.
for the final jacket, which satisfy the ITER targets. JK2LB can be applied to the ITER CS.
Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Isono, Takaaki; Okuno, Kiyoshi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1468 - 1472, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:83.44(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The voltage temperature characteristic curve (V-T curve) observed in the large-current Nb Sn CIC conductor, which was used in the ITER CS Insert, showed a gradual take-off toward normal state as compared with the V-T curve of an individual strand composing the conductor. The gradual take-off corresponds to the reduction in so-called "n-value." In addition, the take-off shifted to lower temperature than that of the strand, namely lower current sharing temperature (Tcs) or lower critical current (Ic). These behaviors cannot be explained by non-uniform magnetic field accompanying enlargement of the conductor, or by non-uniform contact resistance of the conductor terminals. Investigation is therefore required to clarify the condition of each strand in such large CIC conductor, especially in terms of the strain state under large electromagnetic force. In a CIC conductor, since strands are twisted to form a cable, each strand is mechanically supported by a nearby strand at an interval related to the twist pitch. Between two supporting points, the strand is fee to move under transverse force and a cyclic deformation will occur along the strand length. We designed the apparatus to simulate this cyclic deformation and measured the V-T characteristic of the strand. When the strand received the transverse force of about 500 N/m, n-value reduced to one-fifth (about 6) of the original value, which corresponds to that observed in the CS Insert. The level of the force agreed to the electromagnetic force when the CS Insert was energized to 46 kA at 13 T (about 40 A each strand
Sn CIC conductor, which was used in the ITER CS Insert, showed a gradual take-off toward normal state as compared with the V-T curve of an individual strand composing the conductor. The gradual take-off corresponds to the reduction in so-called "n-value." In addition, the take-off shifted to lower temperature than that of the strand, namely lower current sharing temperature (Tcs) or lower critical current (Ic). These behaviors cannot be explained by non-uniform magnetic field accompanying enlargement of the conductor, or by non-uniform contact resistance of the conductor terminals. Investigation is therefore required to clarify the condition of each strand in such large CIC conductor, especially in terms of the strain state under large electromagnetic force. In a CIC conductor, since strands are twisted to form a cable, each strand is mechanically supported by a nearby strand at an interval related to the twist pitch. Between two supporting points, the strand is fee to move under transverse force and a cyclic deformation will occur along the strand length. We designed the apparatus to simulate this cyclic deformation and measured the V-T characteristic of the strand. When the strand received the transverse force of about 500 N/m, n-value reduced to one-fifth (about 6) of the original value, which corresponds to that observed in the CS Insert. The level of the force agreed to the electromagnetic force when the CS Insert was energized to 46 kA at 13 T (about 40 A each strand  13 T = 520 N/m). This suggests that the transverse force acting on each strand can explain the behavior of the V-T curve of the large-current CIC conductor.
13 T = 520 N/m). This suggests that the transverse force acting on each strand can explain the behavior of the V-T curve of the large-current CIC conductor.
Okuno, Kiyoshi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1376 - 1381, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:36.66(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Fusion magnets have major features of a large size, high magnetic field and operation under huge electromagnetic forces together with nuclear radiation. From this point of view, new design principles and fabrication concepts were proposed to build the ITER CS, and a model coil programme was performed for verification. The model coil reached its design point of 13 T and 46 kA, achieving all the goals of the development programme, including the following areas: (1) high-performance Nb Sn strand and mass production of about 26.5 t, (2) high-strength jacket materials (Incoloy 908, titanium, stainless steel) that can undergo Nb
Sn strand and mass production of about 26.5 t, (2) high-strength jacket materials (Incoloy 908, titanium, stainless steel) that can undergo Nb Sn heat treatment, (3) 46 kA cable-in-conduit conductors in a total length of 5 km, (4) insulation materials that can withstand up to 10 MGy radiation dose, (5) fabrication using wind-react-and-transfer method that enables Nb3Sn application to a large magnet with mechanically rigid and high-voltage insulated windings. Results and experiences from the programme are being fed back into the design and QA requirements of the ITER magnets.
Sn heat treatment, (3) 46 kA cable-in-conduit conductors in a total length of 5 km, (4) insulation materials that can withstand up to 10 MGy radiation dose, (5) fabrication using wind-react-and-transfer method that enables Nb3Sn application to a large magnet with mechanically rigid and high-voltage insulated windings. Results and experiences from the programme are being fed back into the design and QA requirements of the ITER magnets.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kizu, Kaname; Miura, Yushi; Ando, Toshinari*; Sakasai, Akira; Matsukawa, Makoto; Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1427 - 1430, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.57(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
 superconducting TF coil for the tight aspect ratio Tokamak power reactor (VECTOR)
superconducting TF coil for the tight aspect ratio Tokamak power reactor (VECTOR)Ando, Toshinari*; Nishio, Satoshi; Yoshimura, Hideto*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1481 - 1484, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:43.14(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Mitchell, N.*; Bessette, D.*; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Matsui, Kunihiro; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Isono, Takaaki; Okuno, Kiyoshi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1410 - 1413, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:48.21(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Cable-in-conduit conductors that consist of about 1,000 Nb Sn strands with an outer diameter of about 0.8mm, have been designed for the TF and CS coils of the ITER. The rated current of these coils is 40 -68kA. Two joint types (Butt and Lap) were developed during the CS Model Coil project. The performance of these joints was evaluated during the operating tests and the satisfied results were obtained. The joints of the TF coils are located outside of the winding in a region where the magnetic field is about 2.1T, a very low value as compared to the maximum field of 11.8T at the winding. The CS joints are located at the coil outer diameter and embedded within the winding pack due to the lack of the space. The maximum fields at the CS joint and winding are 3.5 and 13T, respectively. For the TF coils and the CS, the joints are cooled in series with the conductor at the outlet. The maximum temperature increase due to the joule heating in the joints is set at 0.15K to limit the heat load on the refrigerator. It is shown that both joint types are applicable to the ITER coils.
Sn strands with an outer diameter of about 0.8mm, have been designed for the TF and CS coils of the ITER. The rated current of these coils is 40 -68kA. Two joint types (Butt and Lap) were developed during the CS Model Coil project. The performance of these joints was evaluated during the operating tests and the satisfied results were obtained. The joints of the TF coils are located outside of the winding in a region where the magnetic field is about 2.1T, a very low value as compared to the maximum field of 11.8T at the winding. The CS joints are located at the coil outer diameter and embedded within the winding pack due to the lack of the space. The maximum fields at the CS joint and winding are 3.5 and 13T, respectively. For the TF coils and the CS, the joints are cooled in series with the conductor at the outlet. The maximum temperature increase due to the joule heating in the joints is set at 0.15K to limit the heat load on the refrigerator. It is shown that both joint types are applicable to the ITER coils.
Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Mitchell, N.*; Bessette, D.*; Kubo, Hiroatsu*; Sugimoto, Makoto; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Okuno, Kiyoshi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1405 - 1409, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:59.99(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The ITER Central Solenoid (CS) is 12m high and 4m in diameter. The CS consists of a stack of 6electrically independent modules to allow control of plasma shape. The modules are compressed vertically by a pre-compression structure to maintain contact between modules. The CS conductor is CIC conductor with Nb Sn strands and a steel conduit. The CS model coil and insert coil test results have shown that the conductor design must be modified to achieve an operation margin. This required either to increase the cable diameter or to use strand with a higher current capability. A bronze-process (NbTi)
Sn strands and a steel conduit. The CS model coil and insert coil test results have shown that the conductor design must be modified to achieve an operation margin. This required either to increase the cable diameter or to use strand with a higher current capability. A bronze-process (NbTi) Sn strand is proposed to achieve a higher critical magnetic field. A square conduit with a high Mn stainless steel is proposed as it can satisfy fatigue requirements. The inlets are in the high stress region and any stress intensification there must be minimized. The pre-compression structure is composed of 9tie plates to reduce the stress on the cooling pipes. These design proposals satisfy all ITER operational requirements.
Sn strand is proposed to achieve a higher critical magnetic field. A square conduit with a high Mn stainless steel is proposed as it can satisfy fatigue requirements. The inlets are in the high stress region and any stress intensification there must be minimized. The pre-compression structure is composed of 9tie plates to reduce the stress on the cooling pipes. These design proposals satisfy all ITER operational requirements.
 Al conductor developed for JT-60SC
Al conductor developed for JT-60SCKizu, Kaname; Miura, Yushi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Matsui, Kunihiro; Ando, Toshinari*; Hamada, Kazuya; Hara, Eiji*; Imahashi, Koichi*; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1535 - 1538, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.57(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Matsukawa, Makoto; Miura, Yushi; Shimada, Katsuhiro; Terakado, Tsunehisa; Okano, Jun; Isono, Takaaki; Nunoya, Yoshihiko
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1414 - 1417, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:32.92(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Matsukawa, Makoto; JT-60SC Design Team
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1399 - 1404, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.63(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Tani, Norio; Adachi, Toshikazu*; Igarashi, Susumu*; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Someya, Hirohiko*; Sato, Hikaru*; Kishiro, Junichi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.409 - 412, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:61.57The 3-GeV synchrotron proposed in the JAERI/KEK Joint Project (J-PARC) is a rapid-cycling synchrotron (RCS), which accelerates a high-intensity proton beam from 400-MeV to 3-GeV at a repetition rate of 25-Hz. The 3-GeV synchrotron is used to produce pulsed spallation neutrons and muons. It also works as an injector for a 50-GeV synchrotron. The 3-GeV synchrotron consists of 24 dipole magnets, 60 quadrupole magnets, 18 sextupole magnets and 52 steering magnets. Since the magnets for the 3-GeV synchrotron are required to have a large aperture in order to realize the large beam power of 1 MW, there is a larger fringe field at a pole end than a usual synchrotron magnet. Therefore, it is important to estimate the magnetic field and the effect of multipole component at the fringe field. In this paper, we report the results of the field calculation and mechanical design of RCS magnets.
Tani, Norio; Adachi, Toshikazu*; Someya, Hirohiko*; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Sato, Hikaru*; Kishiro, Junichi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.421 - 424, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:54.64The 3-GeV synchrotron proposed in the JAERI/KEK Joint Project (J-PARC) is a rapid-cycling synchrotron (RCS), which accelerates a high-intensity proton beam from 400-MeV to 3-GeV at a repetition rate of 25-Hz. The 3-GeV synchrotron is used to produce pulsed spallation neutrons and muons. Since the magnets for the 3-GeV synchrotron are required to have a large aperture in order to realize the large beam power of 1 MW, there is a larger fringe field at a pole end than a usual synchrotron magnet. In addition, 25-Hz ac field induces an eddy current in magnet components, magnet end plates and etc. The eddy current induced in the end plates is expected to be large. Therefore, it is important to investigate an effect of large leakage field and eddy current to the beam motion around the magnet end part. We have measured the eddy loss and the eddy field at the edges of the dipole and quadrupole magnets. In this paper, we report the comparison between the results of the measurements and the two-dimensional eddy current model developed for this study.